Concrete Bleeding Explained – Concrete Bleeding is predicted but if it is extreme it may cause issues. This text will clarify Bleeding in detail.
In this article we discussed about removing bleed water from concrete. We also explained effect of segregation and bleeding on quality of concrete and how to fix bleeding in finished concrete. You can check bleeding of concrete slideshare for deatiled info.

What Is Concrete Bleeding?
Bleeding in Concrete – Bleeding in fresh concrete is the process in which free water throughout the mix is pushed upward to the surface because of the settlement of heavier particles similar to cement and water. Bleeding of the water continues till the cement paste has hardened enough to finish the sedimentation process.
The largest factor in bleed water is the water-to-cement ratio. An Increased ratio can result in extreme bleeding. The cement type and fine aggregates can play an important role in figuring out the bleed rate. The less fines you’ve in your mix, the more bleeding will happen.
Factors also include concrete height and strain. The connection between bleed water and concrete heights begins off as linear, however ultimately turns into nonlinear at elevated heights.
Excessive displacement of water by solids in fresh concrete mixture, after the compaction process is called Bleeding in Concrete. Concrete in fresh state is a suspension of solids (aggregates and cement) in water, and after compaction there is a tendency for the solids to settle.
This sedimentation displaces the water and water is pushed upwards. If the process is excessive, the water appears as a layer on the surface. On hot or windy concreting weathers, this bleed water may not be noticed, as it may evaporate faster than bleeding rate.
Why water on top of concrete after pouring ??
This term can be explained as water on top of concrete after pouring. When We pour concrete than sometimes we see the water on the top of concrete, which is actually termed as Concrete bleeding.
There is another similar confusing terminology regarding water, concrete and poring, i.e; concrete curing.
BLEEDING in concrete is a phenomenon in which free water in the mix rises up to the surface and forms a paste of cement on the surface known as “laitance” . Bleeding occurs in concrete when course aggregates tends to settle down and free water rises up to the surface.

Causes Of Concrete Bleeding
Segregation is the cause of bleeding in the concrete mix. Segregation is the phenomena in which heavy aggregate particles settles down, due to settling of heavy particles, water rises up to the surface and forms a layer. This upward movement of water also carries fine particles of cement with it. The top surface of slabs and pavements will not have good wearing quality.
Bleeding will be more frequent on the surface of concrete, when water to cement ratio is higher. The type of cement used, quantity of fine aggregate also plays a key role in rate of bleeding.
Factor Affecting Bleeding in Concrete
- Rate of bleeding will be influenced by drying conditions (wind, and cold days).
- Slower stiffening rate of the concrete, concrete containing a retarder bleed for a longer period of time, increasing the risk of plastic cracking.
- Concrete mix design – Concrete mix design can be adjusted in pumping concrete to minimize segregation or bleeding.
- Sands deficient in fines also tend to increase the bleeding characteristics of the concrete.
- Retarding admixtures in concrete needs careful proportioning to minimize bleeding. Due to the longer initial setting period, concrete remains fresh and can increase bleeding.
- Flowing concrete are more susceptible to segregation and bleeding, it is essential that mix design and proportions take into account the use of a superplasticizer.
Effects caused by Concrete Bleeding
- As a result of bleeding concrete loses its homogeneity.
- Bleeding is liable for inflicting permeability in concrete.
- Bleeding can sometimes reduce the bond between cement paste and aggregate. In this process, bleed water accumulates under the aggregate creating voids resulting in a reduction in strength of the bond between cement paste and aggregate. This process results in the reduction of concrete strength.
- Similarly, water that accumulates beneath the reinforcing bars, notably under the cranked bars, reduces the bond between the reinforcement and concrete.
- If a slip type paver is used for the building of concrete pavement, the bleeding water can cause critical issues. If an excessive amount of of bleeding water accumulates on the surface of the pavement slab, it can lead to the collapse of sides.
- In pavement construction, bleeding water is one of the causes of delayed surface finishing and curing compound application.
Effects Of Bleeding
- Due to bleeding concrete loses its homogeneity.
- Bleeding is responsible for causing permeability in concrete.
- As far as safety is concerned, water that accumulates below the reinforcing bars, reduces the bond between the reinforcement and concrete.
- In the process of bleeding the accumulation of water creates a water voids and reduces bond between the aggregate and cement paste.
- Due to bleeding pumping ability of concrete is reduced.
- Increase in the water-cement ratio at the top.
- The accumulation of water at the top, results in delayed surface finishing.
The biggest factor in bleed water rates is the water-to-cement ratio. A higher ratio can lead to excessive bleeding. The cement type and fine aggregates can play a role in determining the bleed rate. The fewer fines you have in your mix, the more bleeding will occur. Factors also include concrete height and pressure. The relationship between bleed water and concrete heights starts off as linear, but eventually becomes nonlinear at increased heights.
There are also different types of bleeding:
- Normal bleeding refers to a uniform seepage of water over the entire surface of the structure.
- Channel bleeding refers to water rising through particular paths.
Not all bleed water will reach the surface of the concrete. Some bleed water may rise and remain trapped under aggregates and reinforcing. This results in the weakening of the bond between the paste and those elements.
The goal is not to necessarily eliminate bleed water, but rather to manage it to ensure the concrete’s quality. By allowing free water to migrate to a surface and evaporate, the water/cement ratio of the structure decreases, thus decreasing capillary porosity and increasing its density and durability. It can also be useful to aid in finishing operations and reduce plastic shrinkage cracking.
In addition, it is important not to begin finishing operations before most of the bleed water has evaporated. Working the water back into the mix will raise the water/cement ratio in the top surface. That can also result in an increase in permeability. If this surface is exposed to traffic or aggressive environments, this may cause premature delaminating, blistering and cracking.
The use of supplementary cementitious materials can decrease bleeding rates especially when using finer blends. Fly ash can be effective in reducing bleed rates. Silica fume has the largest effect on reducing bleeding.
Micro fibers used in concrete have also been shown to slow down bleed rates as they control the speed of migration of water to the surface while inhibiting the settling of solid particles.
Now Question arises, how to fix bleeding in concrete? Right,
Methods Of Reducing Concrete Bleeding:
- Add minimum water content in the concrete mix, use chemical admixtures to reduce demand to water for a required workability.
- Design the concrete mix properly.
- Use fly ash or other supplementary cementitious materials.
- Using air entraining admixtures is very effective in reducing the bleeding.
- Add more cement in the mix.
- Increase the amount of fine aggregate if sand is coarser (fineness modulus of 2.5 to 2.8 best suited) in mix and reduce aggregate proportionally.
Ways to reduce bleeding in concrete include:
- Reduce water content. Use lower slump mix
- Use finer cements
- Increase amount of fines in the sand
- Use supplementary cementitious materials
- Use air entraining admixtures
Generally, water reducers will decrease bleeding but they may actually end up increasing this rate based on their chemical composition. Air entraining admixtures can also reduce bleeding by increasing cohesion in the fresh concrete and slowing segregation.
How to Reduce Bleeding in Concrete?
Bleeding is the development of a layer of water at the top or surface of freshly placed concrete. The cause of bleeding is the settlement of solid particles (such as cement and aggregates) and the simultaneous upward migration of water. It is worth noting that some bleeding is normal and will not reduce the quality concrete if it is properly placed, finished, and cured.
However, excessive bleeding will increase the water-to-cement ratio in the upper concrete layer near the top surface. This creates a weak top layer with poor durability properties, especially if the finishing operations happen while bleed water is present.
Methods to Reduce Bleeding in Concrete
- Method #1. Reduce the water content (water-to-cementitious material ratio) and slump.
- Method #2. Increase the amount of cement resulting in a reduced water-cement ratio.
- Method #3. Use cementitious materials with finer particles.
- Method #4. Increase the amount of fines in the sand.
- Method #5. Use or increase the amount of supplementary cementing materials such as fly ash, slag cement, or silica fume.
- Method #6. Use chemical admixtures that permit reducing the water to-binder ratios or provide other means capable of reducing the bleeding of concrete.
- Method #7. Use air-entrained concrete.
If you have any questions on this topic or any other technical topic, please contact one of the Technical Department staff at NPCA at (800) 366-7731.
Test for Bleeding of Concrete
Concrete Bleeding Test method provides procedures to be used for determining the effect of variables of composition, treatment, environment, or other factors in the bleeding of concrete. It is also permitted to be used to determine the conformance of a product or treatment with a requirement relating to its effect on bleeding of concrete.
BLEEDING TEST OF CONCRETE (IS:9103-1199) is discussed thoroughly here. From Apparatus to Text result with procedure, which is very easy to understand.
Objective of Concrete Bleeding Test
For determination of relative quantity of mixing water that will bleed from a sample of freshly mixed concrete.
Reference Standard of Concrete Bleeding Test
IS : 9103-1999 – Method of sampling and analysis of concrete.
Apparatus Required for bleeding test of concrete
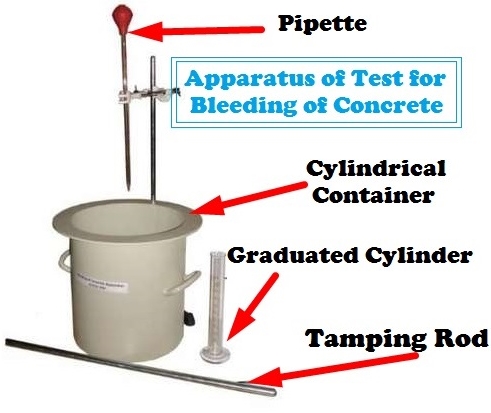
Apparatus and accessory required for bleeding test of concrete are as follows:
- Cylindrical container
- Weighing scale
- Pipette
- Tamping bar
- Graduated cylinder
1. Cylindrical Container
Cylindrical container used for this test is made of steel and has a capacity of 0.01 m3. The inside diameter and the inside height of the cylinder are 250 mm and 280 mm respectively.
2. Weighing Scale
Digital weighing scale of accuracy up to 0.005 is required for weighing specimen samples.
3. Pipette
Pipette is used to draw off the bleed water from specimen.
4. Tamping bar
Tamping bar used in this test is a rounded steel bar of diameter 16 mm and 610 mm length.
5. Graduated Cylinder
Graduated cylinder of 100 cm3 is required to measure the water quantity.
Test Procedure for bleeding test of concrete
- Firstly, take sufficient quantity of freshly mixed concrete of known water content.
- Fill the Cylindrical container with concrete mix in 5 layers of each 50 mm.
- Each layer should be tamped or compacted by giving minimum 60 strokes using tamping bar after filling,
- After compacting the final layer, top surface is leveled and smoothed by troweling.
- Immediately after troweling, note down the time and weigh the container.
- After weighing, place the container in a leveled surface which should be free from vibrations.
- Top of the container should be closed with lid or covered to prevent evaporation of bleed water.
- This test should be conducted at a temperature of 25oc to 29oC.
- For every 10 minutes, draw off the water accumulated on the top surface of concrete using pipette and collect it in graduated cylinder. This should be done for first 40 minutes.
- After 40 minutes, collect water for every 30 minutes and continue until bleeding stops.
- If it is hard to draw off water on flat top surface, slightly tilt the container and collect it.
- Finally note the weight of water collected in graduated jar.
Calculations
Bleeding water % = (B/W) X 100 ——— Equation (1)
Where B = Total quantity of bleeding water
W = Total quantity of water in the concrete mix
Or
Bleeding water percentage of net mixing water contained with in the test specimen is,
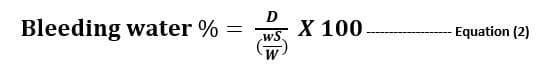
Where, D = Total mass of bleeding water, in Kilogram (Kg)
w = Net mass of water (total water – water absorbed by aggregates)
S = Total mass of concrete mix
W = Total mass of water in the mix
Equation (2) is more accurate than equation (1), since water absorbed by aggregates is considering here.
Safety & Precautions during Concrete Bleeding Test
- To wear hand gloves, safety shoes & apron at the time of test.
- Carefully handle the glass jars during the test time.
- Equipment should be cleaned thoroughly before testing & after testing.
- Petroleum jelly should be applied to the mould.
Several methods were proposed in the past to measure concrete bleeding, but none of them gives complete satisfaction.
The method presented herein consists in sucking water with a pipette, in tracks made on the top surface of concrete just after casting. It takes water evaporation into account. Three tests are carried out simultaneously with three samples of different initial heights.
Comparison of the results leads to know whether bleeding is localised (in channels) or not. The average bleeding rate of tests that exhibit no channel is the major result of the test; it is found to be rather repeatable.
Overall, this method is believed to be more accurate than the previous ones, since any movement of the sample is avoided during test. Also, a double weighing of water is carried out.
what is bleeding in concrete?
Bleeding in concrete is a common issue that occurs when there is an excess of water in the concrete mix. This excess water rises to the surface of the concrete and causes it to become weakened and porous. As a result, the concrete can become more susceptible to damage and may not have the desired strength and durability. To prevent bleeding in concrete, it is important to use the correct amount of water in the mix and to properly cure the concrete after it has been poured. This will help ensure that the concrete has the desired strength and durability.
What is Bleeding property for ternary blended concrete?
The bleeding property of ternary blended concrete refers to the tendency of excess water to rise to the surface of the concrete after it has been placed, causing the surface to become saturated and a water film to form. Bleeding can cause problems with the surface finish of the concrete and can also lead to segregation of the coarse aggregate in the mix.
To reduce the effects of bleeding, the water-cement ratio of the concrete should be kept as low as possible to reduce the amount of excess water in the mix. Additionally, the proportions of the ternary blended materials should be carefully controlled to ensure an even distribution of the cement and other components throughout the mix.